A) MB = MC.
B) MB = 20 and MC = 20.
C) the difference between total benefits and total costs is maximized.
D) of all of the above.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A private good is a good or service for which exclusion:
A) is possible and for which marginal cost of an additional user is zero.
B) is possible and for which marginal cost of an additional user is positive.
C) cannot be applied and for which marginal cost of an additional user is zero.
D) cannot be applied and for which marginal cost of an additional user is positive.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
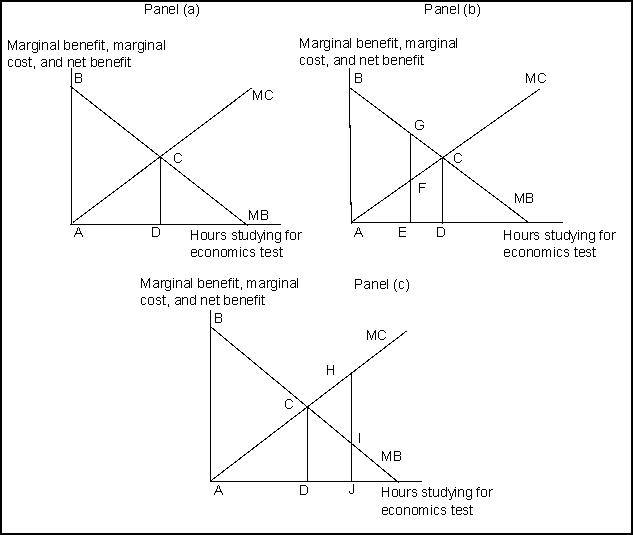 -(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (a) , the maximum net benefit is shown:
-(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (a) , the maximum net benefit is shown:
A) where the level of activity is at D.
B) by the intersection of MB and MC.
C) by the area of triangle ABC.
D) in all of the above cases.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an activity generates external costs, the decisionmakers generating the activity will:
A) be faced with its full costs.
B) be faced with no costs.
C) not be faced with its full costs.
D) be faced with excesive costs.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A characteristic of public goods is that:
A) people pay for them in proportion to the benefits received.
B) the costs of producing them are less than if they were private goods.
C) their benefits cannot be withheld from anyone, regardless of whether the person pays for them.
D) they are produced only by the public sector, not by the private sector.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An industry with external costs produces:
A) a quantity of output that is the socially ideal quantity.
B) a smaller quantity of output than the socially ideal quantity.
C) a larger quantity of output than the socially ideal quantity.
D) the socially ideal quantity of output if a specific subsidy is given to buyers.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a public good?
A) flood control provision
B) police protection
C) a lighthouse
D) postal services
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For markets to operate efficiently, it is necessary that private marginal cost:
A) be equal to output quantity.
B) equal the cost of output.
C) plus external cost be equal to output price.
D) minus external cost be equal to output price.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _______ is the amount by which an additional unit of an activity increases its total benefit.
A) average benefit
B) net benefit
C) marginal benefit
D) top benefit
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Activities of consumers and firms:
A) have benefits but not costs.
B) have costs but not benefits.
C) have both costs and benefits.
D) are too complex to be analyzed with economic theory.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are examples of external cost EXCEPT:
A) smoke nuisance of a factory.
B) zoning restrictions on your property.
C) land defilement from strip mining.
D) weeds on your next-door neighbor's lawn.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the context of public goods and government efforts to correct market failure, economists may tend to be critical of the Endangered Species Act because:
A) economists don't generally care about the environment.
B) species have no economic value.
C) the Act eliminates many activities that would contribute to the total output of the economy.
D) the Act does not generally provide for a weighing of the costs and the benefits of species preservation.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b) at activity level E, _______ , and in Panel (c) at activity level J, _______ .
-(Exhibit: Marginal Benefit, Marginal Cost, and Net Benefit) In Panel (b) at activity level E, _______ , and in Panel (c) at activity level J, _______ .
A) MB < MC; MB < MC
B) MB > MC; MB < MC
C) net benefit is ABGF; net benefit is ABC.
D) there is no deadweight loss; deadweight loss is CHI
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
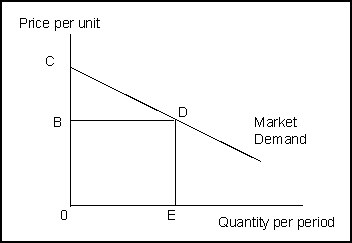 -(Exhibit: Surplus and Demand) The amount by which the total benefits to consumers exceeds their total expenditure is called _______ and is depicted at quantity OE by the area _______ .
-(Exhibit: Surplus and Demand) The amount by which the total benefits to consumers exceeds their total expenditure is called _______ and is depicted at quantity OE by the area _______ .
A) producer surplus; BCD
B) consumer surplus; OCDE
C) consumer surplus; BCD
D) net benefit; OBDE
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Public goods are not sold in efficient quantities in the marketplace because:
A) once supplied to a buyer, they are made available at no cost to someone else.
B) the more one person has, the less another person has.
C) they are usually so costly that only the wealthy can afford them.
D) of none of the above.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the marginal benefit received from a good is less than the marginal cost of production, then:
A) society's well-being can be improved if production increases.
B) society's well-being can be improved if production decreases.
C) society's well-being cannot be improved by changing production.
D) the market is producing too little of the good.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A set of rules that specify the ways in which the resource for which they are defined may be used are:
A) public goods.
B) quasi-public goods.
C) property rights.
D) free-rider rights.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The total benefit of an activity minus its total cost is:
A) net benefit.
B) marginal benefit.
C) marginal cost.
D) utility.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
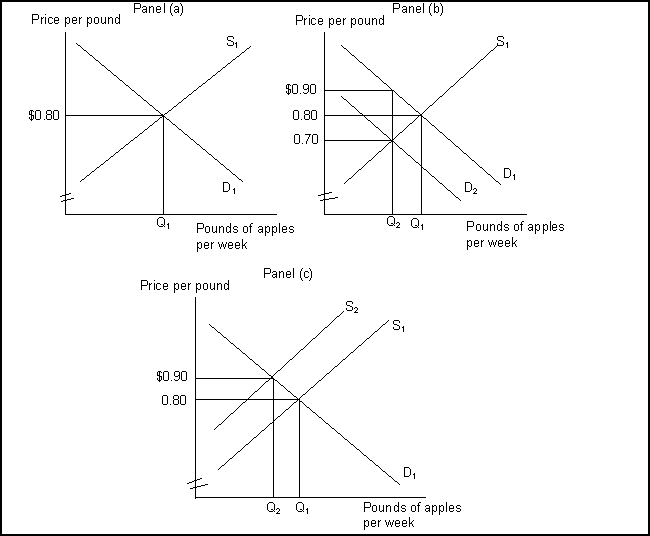 -(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) What is the marginal cost of an extra pound of apples to a producer in Panel(a) ?
-(Exhibit: Markets and Efficiency) What is the marginal cost of an extra pound of apples to a producer in Panel(a) ?
A) It is the value that must be given up to produce an extra pound of apples.
B) It is greater than the price.
C) It must be less than the price.
D) It is the cost of the least satisfactory apples.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 221 - 239 of 239
Related Exams