A) a mutation in a somatic cell
B) a mutation in a liver cell
C) a mutation in a germ-line cell
D) a mutation in a brain cell
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is one way that incorrect nucleotides are removed from a newly synthesized molecule of DNA?
A) Crossing over replaces regions with DNA errors with new segments of DNA.
B) DNA ligases both remove and replace incorrectly positioned nucleotides.
C) Any DNA strand with an error is destroyed, and an entire new strand is synthesized.
D) DNA polymerases remove incorrect nucleotides and replace them with correct ones.
E) DNA ligases remove incorrect nucleotides for replacement by DNA polymerases.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How is the information that specifies a protein stored in DNA?
A) in the arrangement of the sugar-phosphate chain
B) in the types of chemical bonds holding bases together
C) in the sequence of bases
D) in the orientation of the double strands
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the function of DNA polymerase?
A) synthesizing nucleotides from free sugars, phosphates, and bases
B) halting DNA replication if a cell becomes cancerous
C) breaking sugar-phosphate bonds to release free nucleotides for DNA synthesis
D) introducing mutations into DNA for evolutionary adaptation
E) joining together nucleotides as they are base-paired during DNA replication
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A key part of DNA's function is to encode information. In considering how information-rich a particular molecule might be, a question is how many different sequences are possible in a particular length of the molecule. In the case of DNA the four different nucleotides can be arranged in any order. How many different sequences are possible for a DNA strand three nucleotides long?
A) 4
B) 32
C) 16
D) 64
E) 3
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine that the DNA replication error rate for a strain of bacterium that has a defective repair mechanism is 1 in 10 million. If the cell's genome is 5 million nucleotide pairs, how often will the genome sustain a mutation in this strain, keeping in mind that both strands of a DNA molecule are replicated at once?
A) once every five cell divisions
B) once per cell division
C) twice per cell division
D) four times per cell division
E) once every ten cell divisions
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a component of DNA nucleotides?
A) deoxyribose
B) a phosphate group
C) adenine
D) arginine
E) guanine
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The structure of DNA allows the molecule to store information.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Watson and Crick's experiments involved isolating DNA, generating X-ray diffraction images of the DNA, and building a model of its structure.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the relationship between mutations and cancer?
A) Cells do not require mutations to become cancerous but acquire them as they divide.
B) Cells lose the ability to mutate their DNA and evolve once they become cancerous.
C) Some mutations cause cells to lose control over cell division, resulting in cancer.
D) Any point mutation will cause a cell to start proliferating without control, resulting in cancer.
E) Only a mutation can stop a cell once it becomes cancerous.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the relationship between DNA and proteins?
A) Genes are made of proteins that encode the base sequence of DNA.
B) DNA stores the information needed to make proteins.
C) DNA makes up the individual sugar-phosphate-base units of a protein.
D) DNA molecules are the enzymes that synthesize proteins.
E) Proteins store the information needed to make DNA.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Watson and Crick discovered:
A) the structure of DNA.
B) that DNA is the genetic material.
C) X-ray crystallography.
D) that genetic information resides on chromosomes.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The structure of DNA allows the molecule to replicate itself.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two strands of a double helix of DNA are linked by what kind of bond?
A) sugar-phosphate linkages
B) hydrogen bonds between bases
C) hydrogen bonds between sugars and phosphates
D) sugar-base linkages
E) base-phosphate linkages
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A trinucleotide repeat refers to:
A) a nucleotide that is made of three subunits: a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogenous base.
B) a sequence of three nucleotides that repeats and can be involved in genetic diseases.
C) the same nucleotide repeating three times in a row.
D) a nucleotide that contains three bases.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the cause of Huntington disease?
A) a somatic cell mutation that causes cells to proliferate without control
B) a mutation that results in defective DNA polymerase
C) loss of the chromosome with the gene for a blood protein
D) a mutation in which there are repeating groups of three nucleotides
E) a mutation that results in defective amino acid synthesis
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The average mutation rate for DNA replication is 1 mutation for every 10 billion (10,000,000,000) nucleotides of DNA replicated. Yet DNA polymerase makes a mistake during replication at an average of 1 in 100,000 nucleotides. What does this say about DNA replication?
A) Most errors in DNA replication become mutations.
B) The base-pairing rules (A pairs with T and G pairs withC ) Cells are extraordinarily proficient at repairing errors made during DNA replication.
C) prevent any mutations.
D) Cells recognize that a small fraction of mutations are beneficial to organisms and do not repair those.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The building blocks of DNA are:
A) amino acids.
B) enzymes.
C) phosphate groups.
D) nucleotides.
E) bases.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Errors never occur in DNA replication because the DNA polymerases edit out mistakes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Refer to the figure below, and then answer the question that follows. 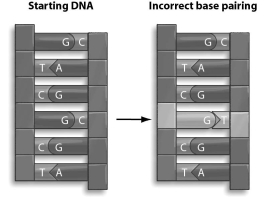 -A mistake is made during DNA replication, so there is incorrect base pairing in the DNA. Depending on how the replication repair mechanism fixes this problem, a point mutation may or may not result. What might the replication repair mechanism do, and would it result in a point mutation?
-A mistake is made during DNA replication, so there is incorrect base pairing in the DNA. Depending on how the replication repair mechanism fixes this problem, a point mutation may or may not result. What might the replication repair mechanism do, and would it result in a point mutation?
A) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
B) The repair mechanism might replace the G with an A, which would result in a point mutation.
C) The repair mechanism might replace the G with a C, which would result in a point mutation.
D) The repair mechanism might replace the T with a G, which would not result in a point mutation.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 71
Related Exams