A) DNA sequences.
B) nutritional modes.
C) choice of habitats.
D) physical appearance.
E) reproductive methods.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please use the following information to answer the questions below.
Diatoms are encased in valves made of translucent hydrated silica whose thickness can vary.The material used to store excess calories can also vary.At certain times,diatoms store excess calories in the form of the liquid polysaccharide laminarin and at other times as oil.The table shows data concerning the density (specific gravity) of various components of diatoms and of their environment.
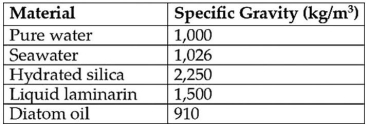 -Judging from the table and given that water's density and,consequently,its buoyancy decreases at warmer temperatures,in which environment would diatoms (and other suspended particles) sink most slowly?
-Judging from the table and given that water's density and,consequently,its buoyancy decreases at warmer temperatures,in which environment would diatoms (and other suspended particles) sink most slowly?
A) cold pure water
B) warm pure water
C) cold seawater
D) warm seawater
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some scientists who study organismal classification believe that green algae should be in an expanded "plant" kingdom called Viridiplantae.If land plants are excluded from this kingdom,then what will be true of it?
A) It will be monophyletic.
B) It will more accurately depict evolutionary relationships than does the current taxonomy.
C) It will be paraphyletic.
D) It will be a true clade.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine you are investigating life in the shallow soils of a forest.In your collected samples,you observe evidence of various single-celled organisms using multiple genetic techniques as well as microscopy.If the organisms you initially assess possess mostly asymmetric or irregular forms,then this particular sample probably has many
A) eukaryotes.
B) archaea.
C) bacteria.
D) prokaryotes.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The oldest fossil eukaryote that can be resolved taxonomically is of
A) a red alga that lived 1.2 billion years ago.
B) a red alga that lived 635 million years ago.
C) a fungus that lived 2 billion years ago.
D) an Ediacaran that lived 550 million years ago.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If true,which of the following is the best evidence that the cyanelles are providing nutrition (in other words,calories) to the surrounding cercozoan?
A) if the cyanelle performs aerobic photosynthesis
B) if the vesicle membrane that surrounds each cyanelle possesses glucose-transport proteins
C) if the cyanelle performs aerobic respiration
D) if radiolabeled 14CO2 enters the cyanelle and if,subsequently,radiolabeled glucose is present in cercozoan cytosol
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term most accurately describes the nutritional mode of healthy P.bursaria?
A) photoautotroph
B) photoheterotroph
C) chemoheterotroph
D) chemoautotroph
E) mixotroph
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following organism pairs is/are an example of secondary endosymbiosis? I.red algae-heterotrophic eukaryote II.green algae-heterotrophic eukaryote III.E.coli bacteria-photosynthetic cyanobacterium IV.Chlamydomonas and Gonium
A) I only
B) III and IV
C) I and II
D) II and III
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is correct with regard to the comparison of secondary endosymbiosis to primary endosymbiosis?
A) In secondary endosymbiosis,an entire free-living alga is ingested into the food vacuole of a heterotrophic eukaryote.
B) In secondary endosymbiosis,an entire free-living alga is incorporated into the mitochondrion a heterotrophic eukaryote.
C) Primary endosymbiosis is the result of alga being engulfed by a cyanobacterium.
D) Primary and secondary endosymbiosis are essential equivalent but occurred at different points in time in the evolution of life.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the mitosomes of Giardia contain no DNA yet are descendants of what were once free-living organisms,then where are we likely to find the genes that encode their structures,and what accounts for their current location there?
A) plasmids;conjugation
B) plasmids;transformation
C) nucleus;horizontal gene transfer
D) nucleus;S phase
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these observations gives the most support to the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotic cells?
A) the existence of structural and molecular differences between the plasma membranes of prokaryotes and the internal membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts
B) the similarity in size between the cytosolic ribosomes of prokaryotes and the ribosomes within mitochondria and chloroplasts
C) the size disparity between most prokaryotic cells and most eukaryotic cells
D) the observation that some eukaryotic cells lack mitochondria
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A P.bursaria cell that has lost its zoochlorellae is said to be aposymbiotic.It might be able to replenish its contingent of zoochlorellae by ingesting them without subsequently digesting them.Which of the following situations would be most favorable to the reestablishment of resident zoochlorellae,assuming that compatible Chlorella are present in P.bursaria's habitat?
A) abundant light,no bacterial prey
B) abundant light,abundant bacterial prey
C) no light,no bacterial prey
D) no light,abundant bacterial prey
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is (are) mutualistic partnerships between a protist and a host organism? I.cellulose-digesting gut protists-wood-eating termites II.dinoflagellates-reef-building coral animals III.Trichomonas-humans IV.algae-certain foraminiferans
A) I only
B) II and IV
C) I,II,and III
D) I,II,and IV
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A large seaweed that floats freely on the surface of deep bodies of water would be expected to lack which of the following?
A) alveoli
B) bladders
C) holdfasts
D) flagella
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chloroplasts of land plants are thought to have been derived according to which evolutionary sequence?
A) cyanobacteria → green algae → land plants
B) cyanobacteria → green algae → fungi → land plants
C) red algae → brown algae → green algae → land plants
D) cyanobacteria → red algae → green algae → land plants
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using dead diatoms to "pump" CO2 to the seafloor is feasible only if dead diatoms sink quickly.Consequently,application of mineral fertilizers,such as iron,should be most effective at times when diatom valves
A) are thickest,and laminarin is being produced rather than oil.
B) are thickest,and oil is being produced rather than laminarin.
C) are thinnest,and laminarin is being produced rather than oil.
D) are thinnest,and oil is being produced rather than laminarin.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When diatoms die,their shells fall to the floor of the ocean or lake that they inhabit and form sediments called diatomaceous earth (DE) .Diatoms can be identified by their shells,and different species of diatoms prefer different water temperatures.The diatoms' porous shells are hard but often break and result in sharp edges.Crop farmers incorporate DE into their soil to help kill insect pests.When insects encounter DE,sharp shell edges cut through their exoskeletons and then softer,broken down DE absorbs insect body fluids,thereby causing the insects to die due to dehydration.Why might farmers who raise large livestock also use DE in the animals' feed?
A) The sharp shells can damage the tissue of intestinal parasites and eventually kill them.
B) DE helps to slow down the livestock's digestion of food,thereby increasing nutrient absorption.
C) The porous nature of the shells in the DE helps keep livestock hydrated.
D) DE encourages growth of "healthy" intestinal bacteria.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells,how did mitochondria originate?
A) from infoldings of the plasma membrane,coupled with mutations of genes for proteins in energy-transfer reactions
B) from engulfed,originally free-living proteobacteria
C) by secondary endosymbiosis
D) from the nuclear envelope folding outward and forming mitochondrial membranes
E) when a protoeukaryote engaged in a symbiotic relationship with a protocell
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is there controversy surrounding the eukaryotic tree?
A) It suggests that the unikonts are evolutionarily derived from the archeplastids.
B) It suggests that amoebozoans are more closely related (evolutionarily) to red algae than green algae.
C) The tree lacks branches for species that have yet to be classified.
D) The root of the tree is uncertain such that it is unknown which supergroup was the first to diverge from all other eukaryotes.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rhizarians that feed using threadlike pseudopodia include which of the following group(s) ? I.forams II.red algae III.cercozoans IV.green algae
A) I and III
B) II and III
C) I and IV
D) II and IV
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 80
Related Exams