A) base.
B) apex.
C) cardiac notch.
D) hilus.
E) epipleurium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figure 23-1 The Upper Airways
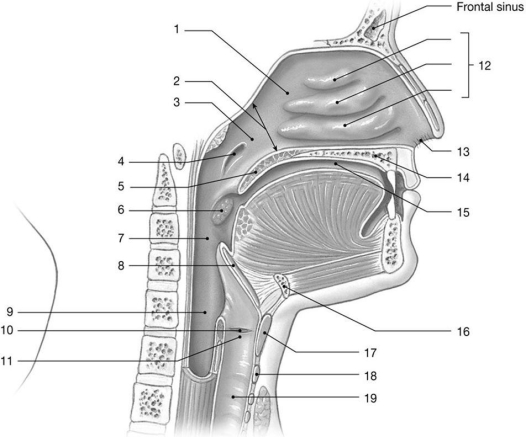 Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "2."
Use Figure 23-1 to answer the following questions:
-Identify the structure labeled "2."
A) olfactory organ
B) oropharynx
C) nasopharynx
D) internal nares
E) nasal sinus
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Harry suffers from cystic fibrosis and has severe breathing difficulties. His problems result from
A) genetic mutation in cilia production.
B) laryngospasms.
C) thick secretions that are difficult to transport.
D) lack of neural control of respiration.
E) reduced mucus secretions in the trachea.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The normal rate and depth of breathing is established by the ________ center(s) .
A) apneustic
B) pneumotaxic
C) DRG and VRG
D) expiratory
E) ventral respiratory
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The actual sites of gas exchange within the lungs are the
A) bronchioles.
B) terminal bronchioles.
C) spaces between the parietal and visceral pleura.
D) blood air barrier of the alveoli.
E) interlobular septa.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the trachea is false?
A) It is lined by pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium.
B) Tracheal cartilages prevent tracheal collapse.
C) It contains many mucous glands.
D) It alters its diameter in response to the autonomic nervous system.
E) It is completely wrapped in smooth muscle.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a reason gas exchange is efficient at the blood air barrier?
A) Partial pressure differences are substantial.
B) Distance is short.
C) Surface area is large.
D) Gap junctions facilitate fast movement.
E) Gases are lipid soluble.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In-Text Figure Based Questions -Inhibition of medulla oblongata chemoreceptors and respiratory muscles has what effect on respiratory rate,elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and arterial PCO2? (Figure 23-26)
A) increased respiratory rate, increased elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and increased arterial PCO2
B) increased respiratory rate, decreased elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and decreased arterial PCO2
C) increased respiratory rate, increased elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and decreased arterial PCO2
D) decreased respiratory rate, increased elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and increased arterial PCO2
E) decreased respiratory rate, decreased elimination of CO2 at alveoli, and increased arterial PCO2
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx constitute the ________ portion of the airway.
A) conducting
B) exchange
C) respiratory
D) sinus
E) primary
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Air that remains in conducting passages and doesn't participate in gas exchange is termed
A) vital capacity.
B) minimal volume.
C) residual volume.
D) functional residual capacity.
E) anatomic dead space.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following descriptions best matches the term external intercostal?
A) accessory muscle of expiration
B) accessory muscle of inspiration
C) primary muscle of inspiration
D) primary muscle of expiration
E) an accessory muscle for both expiration and inspiration
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As an astronaut is lifted into Earth's orbit, what is the first change to take place in response to thedrop in cabin pressure?
A) increased hematocrit
B) renal hypoxia
C) increased alveolar ventilation rate
D) decreased alveolar PO2
E) decreased hemoglobin saturation
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A condition that increases lung compliance is
A) lung cancer.
B) respiratory distress syndrome.
C) loss of surfactant.
D) emphysema.
E) pneumothorax.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common unit of measurement for measuring pulmonary pressures is
A) mm Hg.
B) torr.
C) cm H2O.
D) psi.
E) centigrade.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During quiet breathing,
A) only the internal intercostal muscles contract.
B) inspiration involves muscular contractions and expiration is passive.
C) inspiration is passive and expiration involves muscular contractions.
D) both inspiration and expiration are passive.
E) both inspiration and expiration involve muscular contractions.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the alveolar ventilation rate will
A) decrease the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli.
B) decrease the rate of oxygen diffusion from the alveoli to the blood.
C) increase the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli.
D) decrease the rate of carbon dioxide diffusion from the blood to the alveoli.
E) hardly affect either the partial pressure or diffusion of gases.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Surfactant is produced by what cell type in the alveolus?
A) smooth muscle cells
B) pneumocytes Type I
C) pneumocytes Type II
D) pneumocytes Type I and Type II
E) alveolar macrophages
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when the BPG level is high is
A) greater than hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when the BPG level is low.
B) less than hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when the BPG level is low.
C) equal to hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when the BPG level is low.
D) equal to hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when pH is low.
E) equal to hemoglobin's affinity for oxygen when pH is high.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The paired cartilages that articulate with the superior border of the cricoid cartilage are the ________cartilages.
A) cricothyroid
B) innominate
C) cuneiform
D) corniculate
E) arytenoid
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most important chemical regulator of respiration is
A) oxygen.
B) carbon dioxide.
C) bicarbonate ion.
D) sodium ion.
E) hemoglobin.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 200
Related Exams