A) anchoring junctions.
B) gap junctions.
C) tight junctions.
D) plasmodesmata.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A red blood cell is placed in a solution and it begins to shrink.Which of the following describes the solution?
A) hypertonic
B) isotonic
C) hypotonic
D) supertonic
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Passive carrier molecules often require active carrier proteins to provide amino acids for transport.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hikers can detect a dead skunk along a trail long before they actually see it.What process allows the scent of the skunk to be so widely dispersed?
A) osmosis
B) active transport
C) diffusion
D) transduction
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Epithelial tissue in animals provides a barrier against the invasion of bacteria into the body.Which of the following is most likely to be responsible for creating a tight enough barrier between cells to prevent the passage of bacteria between them?
A) anchoring junctions
B) gap junctions
C) tight junctions
D) plasmodesmata
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
After a sex hormone enters a target cell,it
A) binds to the nucleus.
B) becomes a signaling protein.
C) binds to an internal receptor protein.
D) becomes a gene.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Tight junctions prevent the movement of the extracellular matrix between cells.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine two solutions separated by a selectively permeable membrane that is impermeable to glucose.On one side of the membrane,solution A contains 10 percent glucose and on the other side,solution B contains 25 percent glucose.Which of the following is true?
A) Solution A is hypertonic relative to solution B.
B) The concentration of water is greatest in solution B.
C) Water will move from solution A to solution B.
D) Glucose will diffuse from solution B to solution A.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Active transport requires
A) cellular energy, usually in the form of ATP.
B) thermal energy from the environment.
C) hormonal activation of specific protein carriers.
D) the initial movement of water by osmosis to develop a favorable concentration gradient.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cell surface receptors of chemical messages are made of
A) protein.
B) DNA.
C) lipids.
D) sugars.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You place some Elodea,an aquarium plant,in a hypertonic solution.The cells of the Elodea
A) begin to hemolyze.
B) start to burst.
C) shrink.
D) undergo plasmolysis.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You observe a cell in a solution that swells until it bursts.What you have seen is an instance of osmosis in a(n) ________ solution.
A) hypertonic
B) isotonic
C) hypotonic
D) exotonic
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Imagine a cell needing an essential specific amino acid (one the cell cannot synthesize) .What process could acquire the amino acid most quickly?
A) Phagocytize and digest bacteria, extract the specific amino acid from the residue, and release to the cytoplasm.
B) Place a transporter protein in the membrane that could carry the amino acid across the membrane.
C) Use receptor-mediated endocytosis.
D) Use simple diffusion because the concentration of the needed amino acid will be zero and the gradient will always be maximized.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Soon after a certain molecule enters a cell,the cell begins producing a new type of protein.The molecule was probably a
A) receptor molecule.
B) hydrophilic molecule.
C) carrier protein.
D) hydrophobic hormone.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrophilic signaling molecules
A) move into cells by active transport through carrier protein channels.
B) bind to cell surface receptors and do not enter cells.
C) can passively cross the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptor proteins.
D) move directly into the nucleus through carrier proteins that span the distance from the plasma membrane to the nuclear envelope.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Muscle cells require high concentrations of calcium to function properly.As a result,these cells use ________ transport to move calcium from areas of low concentration outside the cell into the cytoplasm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Plants have hormones.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The arrows in the following figure show the movement of water across the cell wall and plasma membrane of a plant cell. 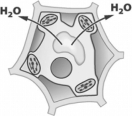 For water to move in the direction indicated,the solution surrounding the cell must be
For water to move in the direction indicated,the solution surrounding the cell must be
A) hypertonic.
B) hypotonic.
C) isotonic.
D) selectively impermeable.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Passive carrier proteins
A) bind to phospholipids in the plasma membrane and move them into the cell.
B) bind to specific external molecules and aid in the formation of vesicles entering the cell.
C) create tunnels in the plasma membrane through which specific solutes can diffuse.
D) change shape upon binding to specific external molecules and then release the molecule on the other side of the membrane.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You observe a vesicle moving toward the plasma membrane from inside a cell.Once it reaches and fuses with the plasma membrane,you will most likely see an example of
A) receptor-mediated endocytosis.
B) pinocytosis.
C) phagocytosis.
D) exocytosis.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 89
Related Exams