A) mitochondria
B) cell walls
C) cytoplasm
D) chloroplasts
E) nuclei
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 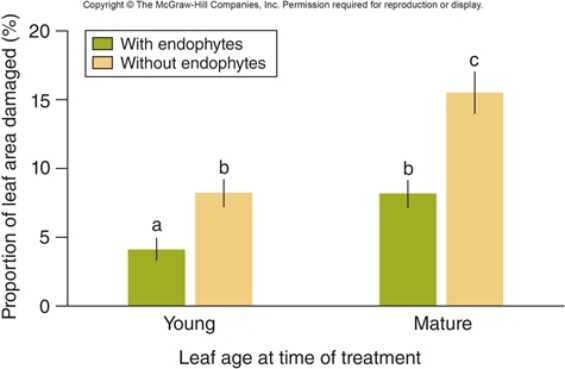 -In the figure,what was the dependent variable?
-In the figure,what was the dependent variable?
A) the percent of the leaf area damaged
B) the age of the leaf
C) the presence or absence of the pathogen Phytophthora
D) the presence or absence of endophyte spores
E) the percent of the leaf area containing endophytes
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zygospores are formed when two haploid hyphae fuse.Zygospores are which of the following?
A) haploid
B) asexual
C) diploid
D) sterile
E) dikaryotic
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sometimes if a person takes an antibiotic to treat a bacterial infection,the yeast Candida can grow out of control and cause a vaginal or intestinal infection.What is the best explanation for this observation?
A) The antibiotic weakens the immune system.
B) There are fewer bacteria present to compete with the yeast.
C) Bacteria normally digest yeast cells.
D) Antibiotics are often contaminated with Candida yeast.
E) The antibiotic causes mutations in the yeast that give the yeast resistance.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The large reproductive structure shown,produced after meiosis in the fungal life cycle,is characteristically covered by a large,flat,shelf,conical,or puffball fruiting body in the phylum 
A) chytridiomycetes.
B) glomeromycetes.
C) zygomycetes.
D) ascomycetes.
E) basidiomycetes.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are lichens a good indicator of environmental quality?
A) If the soil is polluted, they cannot produce roots.
B) They cannot excrete absorbed toxins.
C) They cannot absorb toxins.
D) If the air is polluted, they cannot get enough sunlight for photosynthesis.
E) Toxins inhibit their reproduction.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 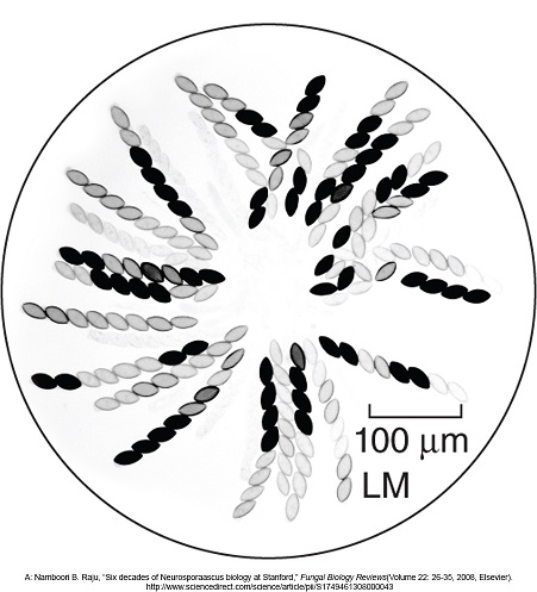 -The organization of the spores would make Neurospora crassa useful for studying which biological process?
-The organization of the spores would make Neurospora crassa useful for studying which biological process?
A) crossing over during meiosis
B) circadian rhythms
C) asexual reproduction
D) gene regulation
E) one gene-one enzyme
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a haploid spore germinates,it goes through mitosis,forming hyphae.The resulting hyphae would be which of the following?
A) gametes
B) dikaryotic
C) haploid
D) diploid
E) zygotes
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:  -Based on the structures of the spores of Neurospora crassa in this figure,in which phylum would it be found?
-Based on the structures of the spores of Neurospora crassa in this figure,in which phylum would it be found?
A) basidiomycetes
B) ascomycetes
C) chytridiomycetes
D) deuteromycetes
E) zygomycetes
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chytridiomycetes produce enzymes that digest cellulose,chitin,and similar molecules.Because of this,they are found in the digestive tract of
A) frogs.
B) people.
C) plants.
D) lichens.
E) ruminants.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The spore-producing structure of aggregated hyphae,as shown in the diagram below,is a 
A) sporophytes.
B) gills.
C) hyphae.
D) fruiting bodies.
E) mycelium.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A dikaryotic stage is common in the life cycle of many plants,protozoans,and fungi.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Ascomycetes are fungi that cause disease and are not beneficial to humans in any way.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Molecular evidence places fungi closer to plants than to animals.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
False
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The familiar growth form represented by edible mushrooms,as well as some poisonous mushrooms,is associated with the ______ phylum.
A) glomeromycetes
B) basidiomycetes
C) zygomycetes
D) ascomycetes
E) chytridiomycetes
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Microscopic reproductive cells produced by most fungi are
A) fruiting bodies.
B) spores.
C) mycelium.
D) gills.
E) hyphae.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
About 80% of all land plants,including grasses,shrubs,and trees,form mycorrhizae.Mycorrhizae are which of the following?
A) mutualistic associations between fungi and plant leaves
B) balanced competitive associations between plants and fungi
C) parasitic associations between fungi and plant leaves
D) mutualistic associations between fungi and plant roots
E) parasitic associations between fungi and plant roots
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A disease-causing fungus found in bird droppings is called
A) Claviceps purpurea.
B) Aspergillus flavus.
C) Coccidioides immitis.
D) Histoplasma capsulatum.
E) Staphylococcus aureus.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Fungi are classified into phyla based on which characteristic?
A) composition of cell wall
B) organelles
C) sexual structures
D) multicellular versus unicellular
E) photosynthesis
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a correct statement?
A) Fungi are heterotrophs, but plants are essentially autotrophs.
B) All of the answer choices are correct.
C) Plants and fungi both carry out photosynthesis.
D) Plants and fungi both have cellulose as the main component of their cell walls.
E) Glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate in both fungi and plants.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 57
Related Exams