A) bundle pricing
B) yield management pricing
C) skimming pricing
D) target return-on-sales pricing
E) penetration pricing
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 Family Dollar Stores Photo
-Consider the photo above.Family Dollar Stores,like 99¢ Stores,use what type of pricing policy?
Family Dollar Stores Photo
-Consider the photo above.Family Dollar Stores,like 99¢ Stores,use what type of pricing policy?
A) target
B) customary
C) flexible
D) one
E) below-market
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
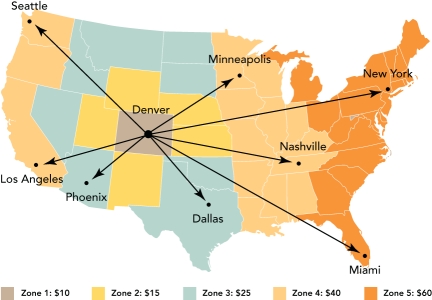 Geographical Pricing Map B
-pricing strategy where the buyer is allowed to deduct freight expenses from the list price of the goods so the seller pays the transportation costs is referred to as
Geographical Pricing Map B
-pricing strategy where the buyer is allowed to deduct freight expenses from the list price of the goods so the seller pays the transportation costs is referred to as
A) FOB factory pricing.
B) FOB absorption pricing.
C) FOB origin pricing.
D) basing-point pricing.
E) FOB with freight-allowed pricing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
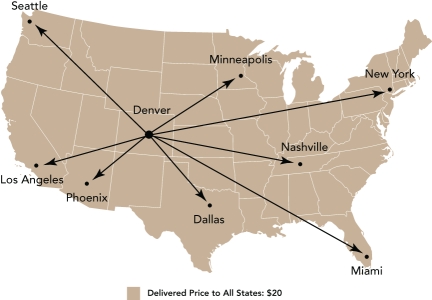 Geographical Pricing Map A
-After extensive analysis,a mail order company has decided to embark on a policy of multiple-zone pricing.In which step of the price-setting process would the mail order firm have made this decision?
Geographical Pricing Map A
-After extensive analysis,a mail order company has decided to embark on a policy of multiple-zone pricing.In which step of the price-setting process would the mail order firm have made this decision?
A) make special adjustments to the list or quoted price
B) select an approximate price level
C) estimate demand and revenue
D) identify price constraints and objectives
E) set list or quoted price
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Supermarket managers use standard markup pricing because it is particularly suited to situations when
A) there is a large number of products and estimating the demand for each would be difficult and time consuming.
B) there is a large number of product lines, all with basically the same product attributes.
C) there is a specific profit goal that needs to be achieved.
D) there is a policy of selling every item in a product line at the same price regardless of the product class.
E) the products are perishable or seasonal.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ad campaign by Suave shampoo asked television viewers to identify the heads of hair of women who used Suave shampoo and conditioner and those that used the much more expensive salon hair-care products.The idea of the ad was that no one could tell which woman used the much cheaper Suave brand.By making price its selling point,Suave is most likely using __________.
A) above-market pricing
B) loss-leader pricing
C) prestige pricing
D) skimming pricing
E) below-market pricing
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Reductions in unit costs for a larger order are referred to as
A) promotional allowances.
B) quantity discounts.
C) economic order discounts.
D) penetration pricing.
E) case allowances.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
setting of prices for all items in a product line to cover the total cost and produce a profit for the complete line,not necessarily for each item,is referred to as
A) line item pricing.
B) product-line pricing.
C) price lining.
D) customary pricing.
E) discretionary pricing.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
unique feature of the Robinson-Patman Act is that it allows for price differentials to different customers under several conditions.Which of the following practices would be permitted?
A) Using price differentials when price differences are given on the basis of other family businesses.
B) Using price differentials when charging different prices to different buyers for goods of like grade or quality.
C) When price differences are quoted to selected buyers in good faith to meet competitors' prices and are not intended to injure competition.
D) Using price differentials when charging different prices on the basis of religious affiliation.
E) Using price differentials when charging the original price for refurbished goods that have been damaged or used and returned but repaired according to company specifications.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marginal analysis refers to
A) a continuing, concise trade-off of incremental costs against incremental revenues.
B) the change in total cost that results from producing and marketing one additional unit of a product.
C) a technique that analyzes the relationship between total revenue and total cost to determine profitability at various levels of output.
D) a continuing concise trade-off of incremental ROI and incremental ROA.
E) a technique that analyzes the relationship between revenues, profit, and market share relative to changes in market growth rates.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
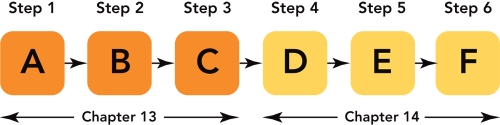 Figure 14-1
-According to Figure 14-1 above,"E" represents which step in the price-setting process?
Figure 14-1
-According to Figure 14-1 above,"E" represents which step in the price-setting process?
A) set list or quoted price
B) select an approximate price level
C) scan competitors for prices of similar products or services
D) determine cost, volume, and profit relationships
E) identify pricing objectives and constraints
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements regarding price lining is most accurate?
A) In order for price lining to be effective, there should be at least 10 specified price points.
B) Price lining assumes that demand is inelastic at each price point but elastic between price points.
C) Price lining assumes that demand is elastic at each price point but inelastic between price points.
D) Price lining is the preferred pricing strategy for governmental contracts.
E) Price lining is the same as above-, at-, or below-market pricing.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
the cash discount terms for a $500 purchase are 4/10 net 30,the number $500 refers to
A) the original price owed on the merchandise.
B) the total amount owed if paid within 10 days.
C) the total discount in dollars if the bill is paid on time in 30 days.
D) the manufacturer's suggested wholesale price.
E) the total penalty in dollars if the bill is paid after 10 days.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
a __________ pricing strategy,a price setter stresses the __________ side of the pricing problem.
A) demand-oriented; cost
B) supply-oriented; target ROI
C) competition-oriented; marketing channel
D) cost-oriented; cost
E) profit-oriented; revenue
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Skimming pricing is considered to be a __________ approach to pricing.
A) demand-oriented
B) cost-oriented
C) profit-oriented
D) competition-oriented
E) service-oriented
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
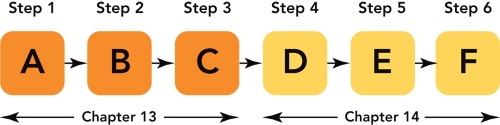 Figure 14-1
-Figure 14-1 above represents the six steps in the price-setting process.Which letter represents the step where a firm would balance incremental costs and revenues?
Figure 14-1
-Figure 14-1 above represents the six steps in the price-setting process.Which letter represents the step where a firm would balance incremental costs and revenues?
A) "E"
B) "F"
C) "D"
D) "C"
E) "A"
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a cost-oriented pricing method?
A) loss leader pricing
B) standard markup pricing
C) at-, above-, or below-market pricing
D) price lining
E) penetration pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
3M launched its premium Greptile Grip golf glove consisting of the highest quality Cabretta sheep leather,it suggested a retail price range of $16.95 to $19.95.Golf glove marketer Bionic had introduced its Classic at $24.95 and its Pro at $39.95,while FootJoy launched its Pure Touch Limited at $28.00 and its SciFlex at $18.00.Other competitors focused on price/value at three price points: $6.00-$9.99,$10.00-$16.99,and $17.00 and up.These statements suggest that 3M has been pursuing a __________ method of selecting an approximate price level.
A) competition-based
B) profit-oriented
C) cost-oriented
D) demand-oriented
E) experience-oriented
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
movement from point A to point B in Figure 14-3A above shows
A) skimming demand.
B) penetration demand.
C) that buyers see the product as a bargain and buy more.
D) that buyers become dubious about the quality and prestige and buy less.
E) a downturn in the economy.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
pricing method where all buyers pay the same delivered price for the products,regardless of their distance from the seller,is referred to as __________.
A) single-zone pricing
B) multiple-zone pricing
C) freight-absorption pricing
D) FOB origin pricing
E) basing-point pricing
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 398
Related Exams